China's timber and household industry faces new challenges as EU implements zero-deforestation bill
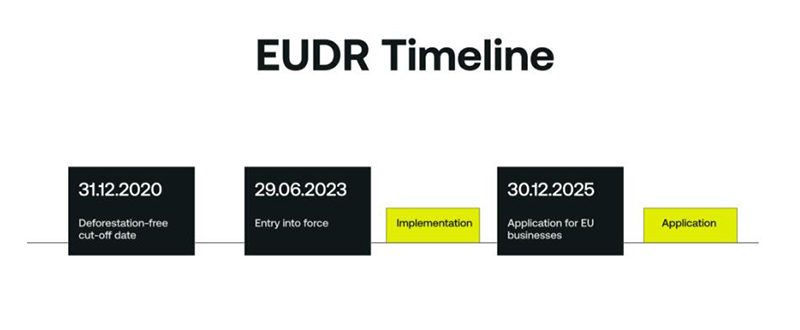
In the face of the continuous decline of global forest resources and the deterioration of the ecological environment, the European Union has recently formally introduced the European Union Zero Deforestation Act (EUDR), which aims to ensure that products sold in its markets do not trigger deforestation or degradation through a series of stringent supply chain due diligence measures. The Act, which will be fully implemented from December 30, 2024, imposes higher traceability and compliance requirements on a wide range of commodities, including timber, cattle, cocoa, Wooden Modern Napkin Holder, Wooden paper roll holder, etc., and will have a direct impact on the mode of operation and trade flow of the relevant industries around the world.

The implementation of the EU Zero Deforestation Act marks an important step in the EU's global environmental protection and sustainability policy. According to the Act, any goods sold in the EU market whose production is related to deforestation or forest degradation will be subject to strict legal restrictions. The move not only covers products directly related to forest destruction, but also affects downstream industries that use these products as raw materials, including the furniture, paper and rubber industries.

As China is one of the world's largest producers and exporters of wood products, the implementation of this bill will have a particularly far-reaching impact on our wood and home furnishing industries. According to statistics, the export volume of China's forest products occupies an important proportion of the international market, and the EU is one of the major export destinations. The implementation of the bill means that when exporting to the EU, China's timber and related companies will need to provide detailed supply chain due diligence reports to prove that their products are from legitimate sources and meet environmental protection standards.
For China's timber and home furnishings industry, which has already been affected by both international trade friction and domestic market adjustments, the implementation of the EUDR has undoubtedly brought new challenges. Enterprises need to respond to this change by strengthening internal management and enhancing supply chain transparency. Industry experts suggest that companies should take this opportunity to optimize supply chain management, improve the supervision of raw material procurement, and actively promote the interface with international certification standards, such as FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) forest certification.

At the same time, the government is also taking measures to help local enterprises adapt to this change, for example, by providing policy interpretation, technical training and financial subsidies to support enterprises in improving their production and management processes to meet the new requirements of the international market. This not only helps reduce compliance risks for enterprises, but also promotes the sustainable development of China's forestry and wood products industry.

Facing the challenges of the new EU regulations, China's wood and household industry stands at a new historical starting point. How to realize the transformation from “Made in China” to “Created in China” through innovation and upgrading will be the key to the future development of the industry.
